聊聊Node中的url模块和querystring模块

url模块和querystring模块是非常重要的两个URL处理模块。在做node服务端的开发时会经常用到。
url
在介绍url模块之前我们先来一张图,看懂了这张图对于url这个模块你就基本上没什么问题了。

我们来解释下各自的含义
- protocol:协议,需要注意的是包含了
:,并且是小写的。【相关教程推荐:、】 - slashes:如果
:后面跟了两个//,那么为true。 - auth:认证信息,如果有密码,为
usrname:passwd,如果没有,则为usrname。注意,这里区分大小写。 - host:主机名。注意包含了端口,比如
ke.qq.com:8080,并且是小写的。 - hostname:主机名,不包含端口,并且是小写的。
- port: 端口号。
- path:路径部分,包含search部分。
- pathname:路径部分,不包含search部分。
- search:查询字符串,注意,包含了
?,此外,值是没有经过decode的。 - query:字符串 或者 对象。如果是字符串,则是
search去掉?,其余一样;如果是对象,那么是decode过的。 - hash:哈希部分,注意包含了
#。 - href:原始的地址。不过需要注意的是,
protocol、host会被转成小写字母。
下面我们来讲解下它的三个常用方法
parse(urlString, parseQueryString, slashesDenoteHost)
该方法将url字符串,解析成object,便于开发者进行操作。
const url = require("url"); const str = "http://user:password@randy.com:8080/index.html?nick=%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87#part=1"; const obj = url.parse(str); console.log(obj);
输出
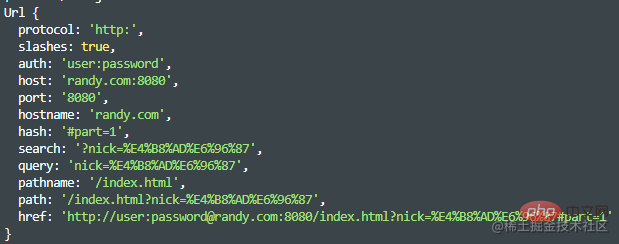
该方法还支持传递另外两个参数,parseQueryString和slashesDenoteHos
parseQueryString:(默认为false)如为false,则urlObject.query为未解析的字符串,比如nick=%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87,且对应的值不会decode;如果parseQueryString为true,则urlObject.query为object,比如{ nick: '中文' },且值会被`decode;
const url = require("url"); const str = "http://user:password@randy.com:8080/index.html?nick=%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87#part=1"; const obj2 = url.parse(str, true); console.log(obj2);
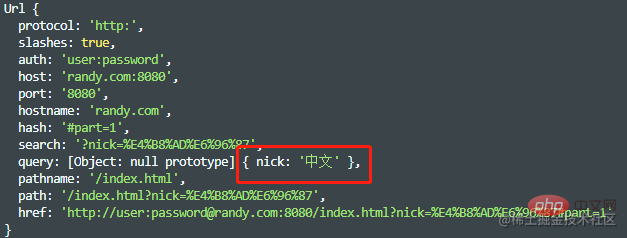
slashesDenoteHos:(默认为false)如果为true,那么类似//randy/nick里的randy就会被认为是hostname;如果为false,则randy被认为是pathname的一部分。
光看起来可能不太理解这句话的含义,下面笔者举个例子我相信你们就明白了。
const str2 = "//randy/nick"; const obj3 = url.parse(str2, true, false); console.log(obj3); const obj4 = url.parse(str2, true, true); console.log(obj4);
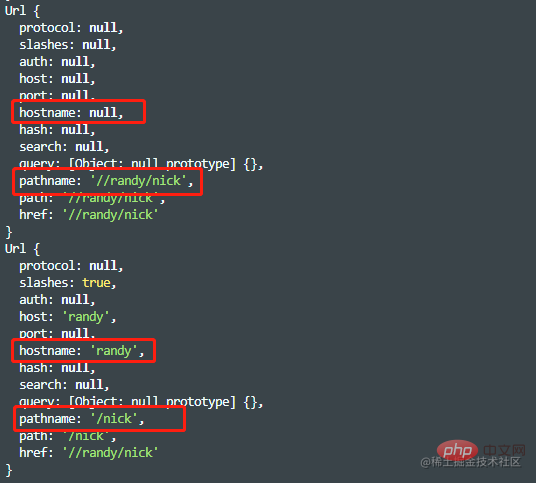
format(urlObject)
这个方法就是parse的反向操作。将对象转成url字符串。
const pathObj = {
protocol: "http:",
slashes: true,
auth: "user:password",
host: "randy.com:8080",
port: "8080",
hostname: "randy.com",
hash: "#part=1",
search: "?nick=%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87",
query: "nick=%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87",
pathname: "/index.html",
path: "/index.html?nick=%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87",
href: "http://user:password@randy.com:8080/index.html?nick=%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87#part=1",
};
console.log(url.format(pathObj)); // http://user:password@randy.com:8080/index.html?nick=%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87#part=1resolve(from, to)
该方法用于解析相对于基本URL的目标URL。
console.log(url.resolve("/one/two/three", "four")); // /one/two/four console.log(url.resolve("http://example.com/", "/one")); // http://example.com/one console.log(url.resolve("http://example.com/one", "/two")); // http://example.com/two console.log(url.resolve("http://example.com/one/ddd/ddd/ddd", "./two")); // http://example.com/one/ddd/ddd/two console.log(url.resolve("http://example.com/one/ddd/ddd/ddd", "../two")); // http://example.com/one/ddd/two console.log(url.resolve("http://example.com/one/ddd/ddd/ddd", ".../two")); // http://example.com/one/ddd/ddd/.../two
querystring
querystring这个模块,也是用来做url查询参数的解析。这里我们重点分析下它的parse和stringify两个方法。
parse(str, sep, eq, options)
parse是将查询字符串转成对象类型,并且也会decode。
const querystring = require("querystring");
const str = "nick=randy&age=24&nick2=%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87";
const obj = querystring.parse(str);
console.log(obj); // { nick: 'randy', age: '24', nick2: '中文' }下面我们再来看看它的第二和第三个参数。其实相当于可以替换&、=为自定义字符,下面笔者举个例子就很快明白了。
const str1 = "name-randy|country-cn";
const obj1 = querystring.parse(str1);
console.log(obj1); // { 'name-randy|country-cn': '' }
const obj2 = querystring.parse(str1, "|", "-");
console.log(obj2); // { name: 'randy', country: 'cn' }相当于把&替换成了|,把=替换成了-。笔者感觉配到这种情况应该不多。
stringify(obj, sep, eq, options)
这个方法就是上面parse的反向操作。下面咱们直接上例子
const obj3 = {
nick: "randy",
age: "24",
};
const str4 = querystring.stringify(obj3);
console.log(str4); // nick=randy&age=24这个方法也是支持自定义分割符的。
const obj5 = {
name: "randy",
country: "cn",
};
const str6 = querystring.stringify(obj5, "|", "-");
console.log(str6); // name-randy|country-c更多node相关知识,请访问:!
以上就是聊聊Node中的url模块和querystring模块的详细内容,更多请关注本站点其它相关文章!
本文地址:https://www.stayed.cn/item/27557
转载请注明出处。
本站部分内容来源于网络,如侵犯到您的权益,请 联系我

我的博客
人生若只如初见,何事秋风悲画扇。
我的标签
随笔档案
- 2024-02(2)
- 2023-06(1)
- 2023-05(1)
- 2023-04(14)
- 2023-03(3)
- 2023-01(6)
- 2022-12(5)
- 2022-11(5)
- 2022-07(2)
- 2022-06(4)
- 2022-05(3)
- 2022-03(1)
- 2021-12(6)
- 2021-11(1)
- 2021-10(3)
- 2021-09(5)
- 2021-07(5)
- 2021-02(2)
- 2021-01(7)
- 2020-12(18)
- 2020-11(14)
- 2020-10(12)
- 2020-09(10)
- 2020-08(22)
- 2020-07(2)
- 2020-06(1)
- 2020-04(5)
- 2020-03(9)
- 2020-02(7)
- 2020-01(9)
- 2019-12(8)
- 2019-11(10)
- 2019-10(11)
- 2019-09(17)
- 2019-08(16)
- 2019-07(6)
- 2019-06(3)
- 2019-04(1)
- 2019-03(8)
- 2019-02(5)
- 2019-01(1)
- 2018-11(2)
- 2018-10(3)
- 2018-09(1)
- 2018-08(3)
- 2018-07(3)
- 2018-06(7)
- 2018-04(4)
- 2018-03(5)
- 2018-02(4)
- 2018-01(22)
- 2017-12(3)
- 2017-11(5)
- 2017-10(15)
- 2017-09(26)
- 2017-08(1)
- 2017-07(3)